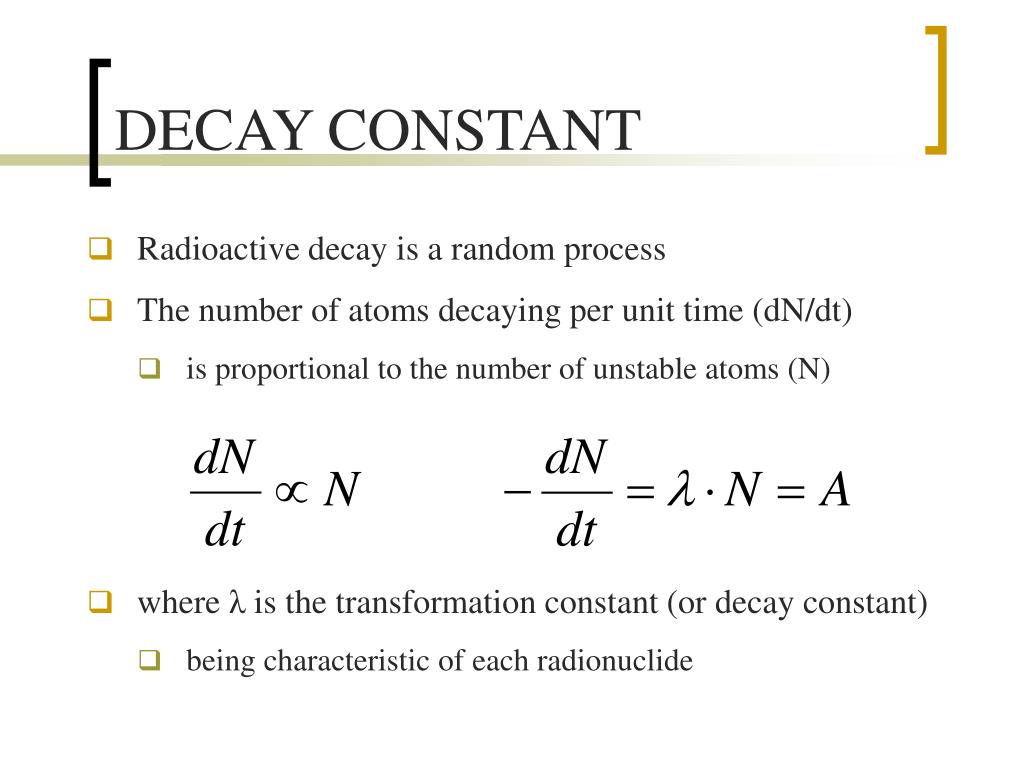
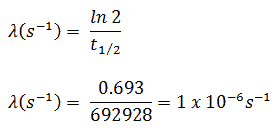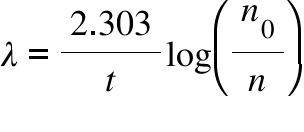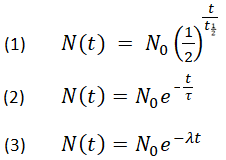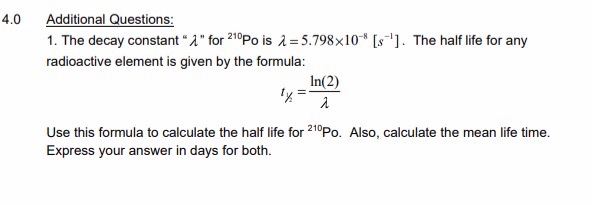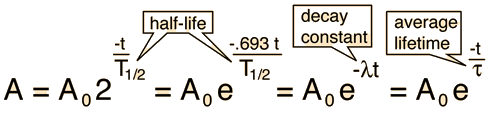Decay Constant

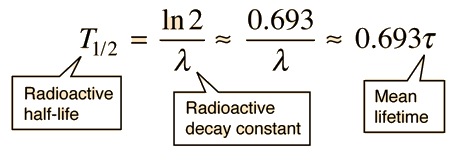
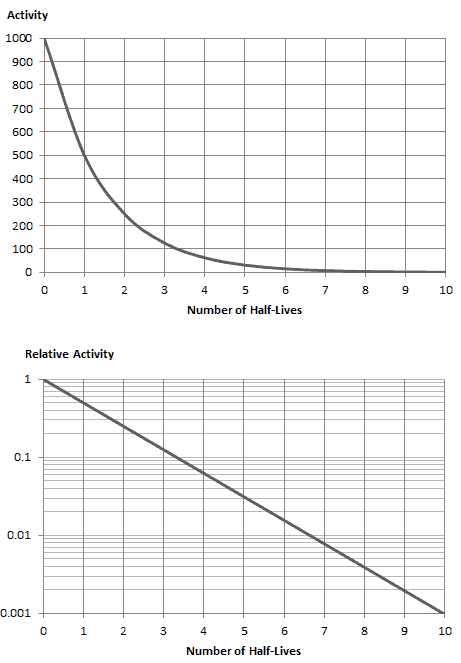
The radioactive decay law states that the probability per unit time that a nucleus will decay is a constant independent of time.
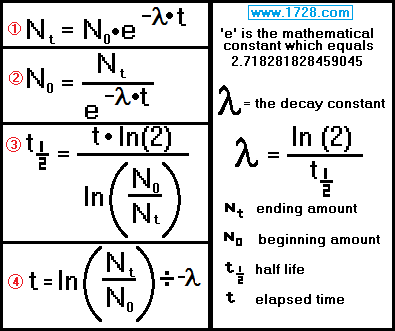
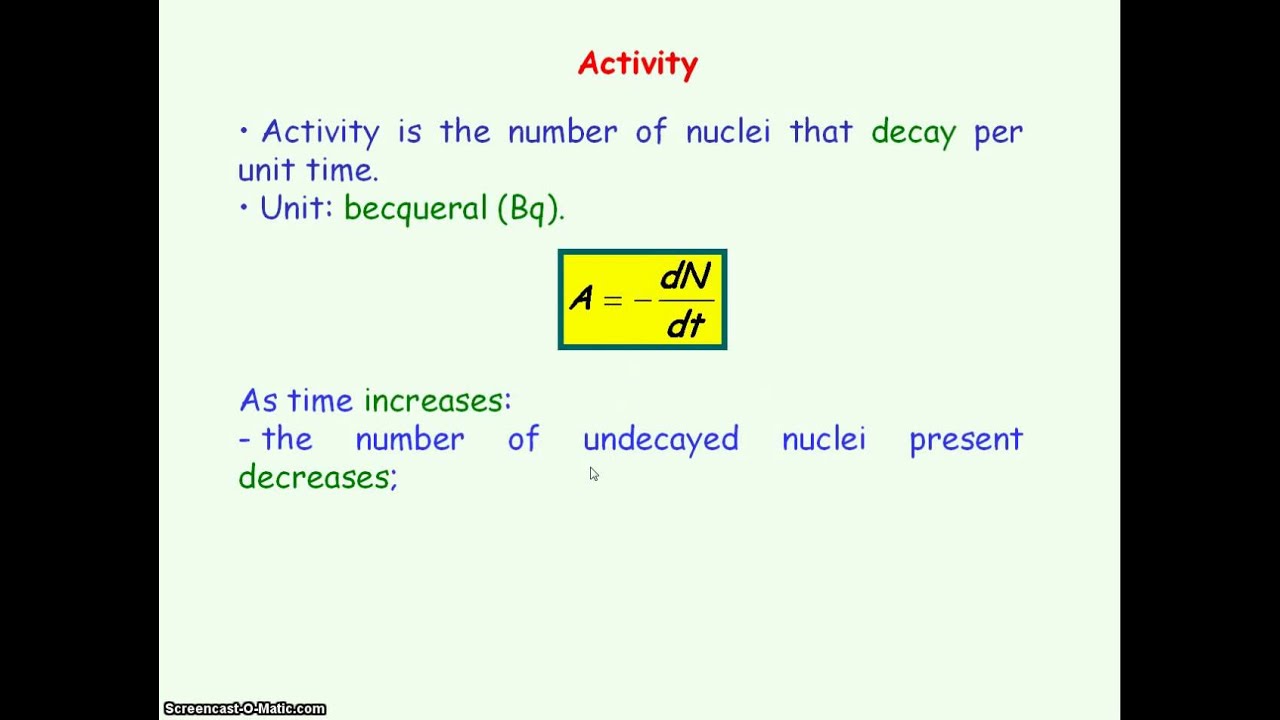
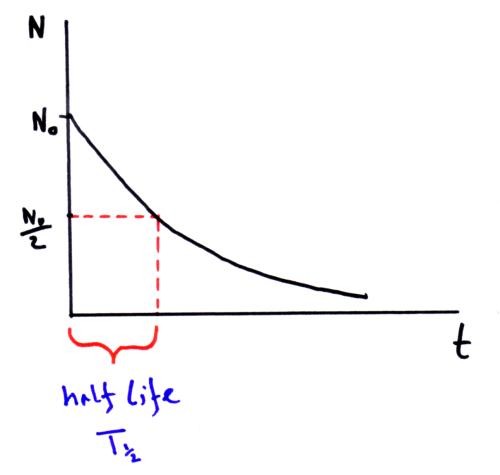
Decay constant. Decay constant determines the rate of decay. Suppose n is the size of a population of radioactive atoms at a given time t and d n is the amount by which the population decreases in time d t. Decay constant is denoted by λ lambda. The rate of decomposition is mainly governed by a user defined decay constant and adjusted according to monthly temperature and precipitation.
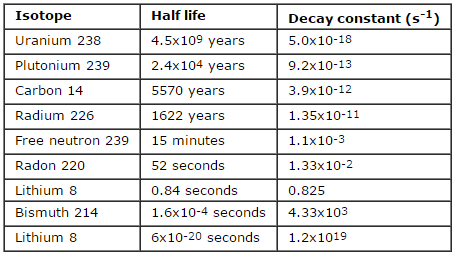
This constant probability may vary greatly between different types of nuclei leading to the many different observed decay rates. This constant is called the decay constant and is denoted by λ lambda. The radioactive decay law states that the probability per unit time that a nucleus will decay is a constant independent of time. The constant ratio for the number of atoms of a radionuclide that decay in a given period of time compared with the total number of atoms of the same kind present at the beginning of that period.
Disintegration constant radioactive constant. Decay constant proportionality between the size of a population of radioactive atoms and the rate at which the population decreases because of radioactive decay. Then the rate of change is given by the equation d n d t λ n where λ is the decay constant. A decay constant which is unique for each radioactive isotope chapter 13 stable and radioactive isotopes rusle computes decomposition of organic matter in the ground cover and the soil biomass pools.
This constant probability may vary greatly between different types of nuclei leading to the many different observed decay rates. This constant probability may vary greatly between different types of nuclei leading to the many different observed decay rates.